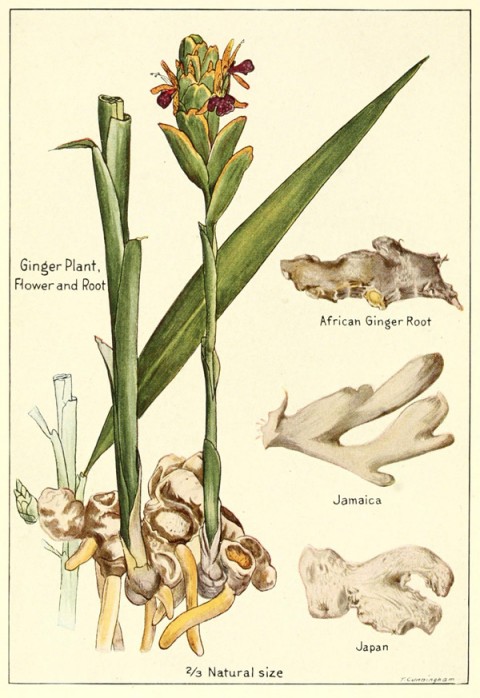
Ginger
Ginger
is the rhizome of the plant Zingiber officinale, consumed as a delicacy, medicine, or spice. It lends its name to its genus and family (Zingiberaceae). Other notable members of this plant family are turmeric, cardamom, and galangal. Ginger cultivation began in South Asia and has since spread to East Africa and the Caribbean.
The English name ginger comes from French: gingembre, Old English: gingifere, Medieval Latin: gingiber, Greek: zingíberis (ζιγγίβερις). Ultimately the origin is from Tamil word ‘inji ver’ (இஞ்சி வேர்) or Malayalam word ‘inji veru’ (ഇഞ്ചി വേര്). The botanical term for root in Tamil is ver (வேர்) and Malayalam is veru (വേര്), hence inji root or inji ver.
Ginger tea is a beverage in many countries, made from ginger root. In China, the tea is made by boiling peeled and sliced ginger to which brown sugar is often added. Sliced orange or lemon fruit may also be added to give a flavor, and it may be consumed both hot or cold. In Korean cuisine, ginger tea is called saenggang cha (생강차). It can be made either by boiling the ginger or by mixing hot water and preserved sweetened ginger. For the latter, sliced ginger root is stored with honey for a few weeks like jam. In Japanese cuisine it is called shōgayu (生姜湯). In Philippine cuisine it is called salabat and served in the relatively cold month of December. From its main ingredient ginger tea derives a flavor that is spicy and stimulating. Ginger, known as Adarak in Hindi, is used frequently in tea made in all parts of India as well.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ginger
Foto:
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ginger-plant-flower-root.png